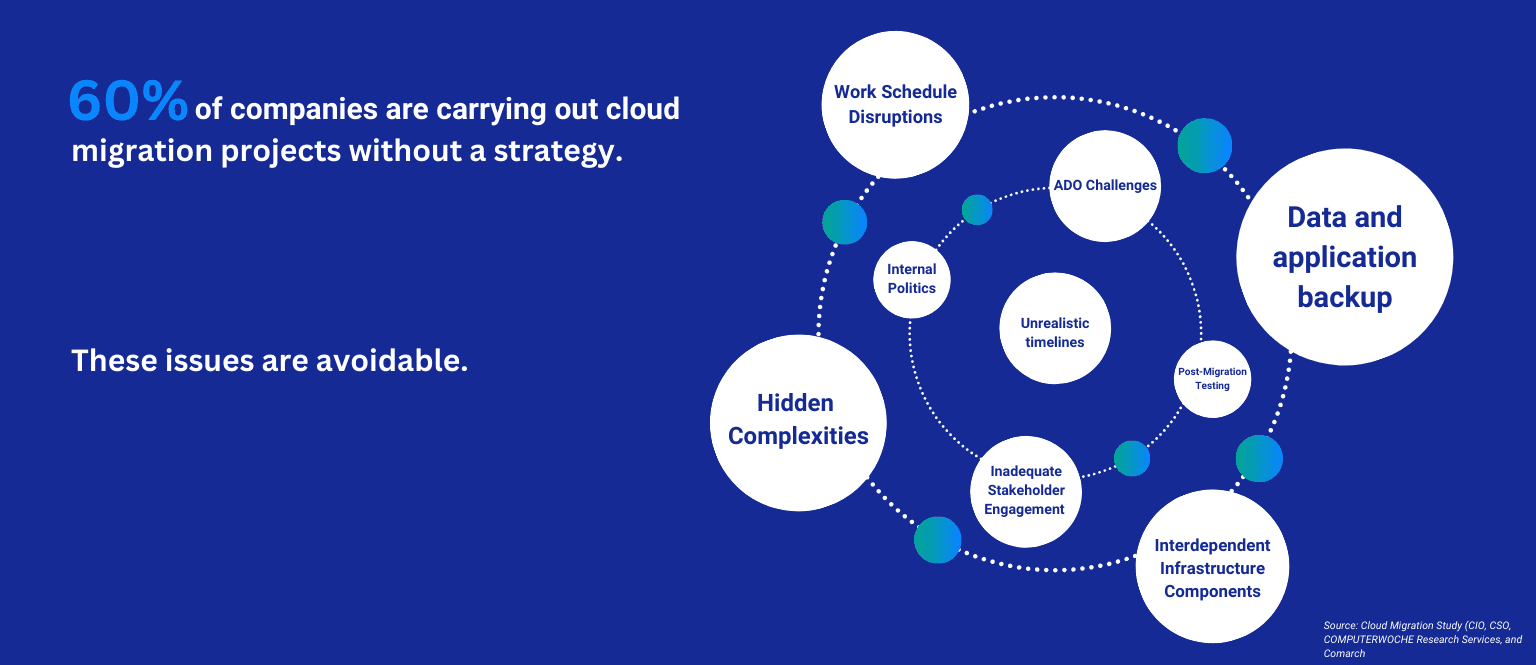
Throughout the data center migration planning phase, compliance should be top-of-mind. The list of standards, guidelines, and regulatory bodies is exhaustive – not to mention critical.
Typically, healthcare organizations, financial institutions, and tech companies face the most rigorous compliance standards. Let's explore which compliance standards these industries will face.
SSAE 18 (Statement on Standards for Attestation Engagements)
SSAE 18, governing internal controls over financial reporting, ensures transparency in business and compliance interactions. Particularly vital for service organizations, it is typically reviewed as part of a SOC 1 report.
SOC Reports
Service Organization Control (SOC) is a prevalent measure of data center security controls. There are two forms of SOC audits, Type I refers to the effectiveness of security controls at a specific point in time. Type II audits will evaluate the effectiveness of security controls over a set period of time (typically 6-12 months).
- SOC 1: This assessment evaluates the effectiveness of a service organization's internal controls concerning financial reporting, aiming to safeguard client data.
- SOC 2: Conducted through an audit, SOC 2 scrutinizes internal controls pertaining to security, covering aspects such as data availability, confidentiality, privacy, and processing integrity.
- SOC 3: Resembling SOC 2, SOC 3 verifies the adequacy of internal security controls. However, it differs by providing a report that doesn't disclose specific details about the organization's systems. Unlike SOC 1 and SOC 2, SOC 3 reports are public-facing, serving as a means for potential customers to gauge compliance without divulging mission-critical or proprietary information. Notably, SOC 3 reports do not have designated Type I or Type II classifications.
ISO/IEC 27001: 2013 (International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission)
Integral to risk management involving private and sensitive data, ISO/IEC 27001 assesses how well an organization identifies risks, addresses access and authentication vulnerabilities, and provides ongoing training to ensure customer information security.
HIPAA/HITECH (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act/Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act)
Designed to protect personal health data, HIPAA/HITECH is crucial for the digitized healthcare industry, covering PII and ePHI. Specific attestation for this compliance standard is AT-C 105 & 205.
PCI DSS 4.0 (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
Imposing strict controls on handling personal financial data in electronically processed credit card payments, PCI DSS 4.0 is essential for any entity processing credit card payments or storing financial data electronically.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
As a comprehensive data privacy and security law, GDPR has been impacting organizations conducting business with EU and UK citizens since 2018. It grants EU citizens the right to control their data handling, including notification when data is collected and the "right to be forgotten." Data centers must facilitate access to data for EU citizens and adhere to data security requirements globally.
The consequences of regulatory non-compliance are incredibly steep, even post-GDPR. Look no further than the costly repercussions of these breaches:
- Amazon: $877 million GDPR fine
- Zoom: $85 million settlement
- Netherlands Tax & Customs Administration: $4 million GDPR fine
- WhatsApp: $244 million in combined fines from GDPR and the Irish Data Protection Commission