UWB Technology: What is it and How Can we Use it?
- Published
- 10 min reading
Let’s take a trip in a time machine today, all the way back to the early 20th century. That’s when the use of a wireless technology started, the development of which has resulted in the ultra-wideband technology which is increasingly popular these days.
What is UWB?
The father of wireless technologies is considered to be the Italian designer Guglielmo Marconi, whose work made it possible to send the first radio transmission across the Atlantic Ocean in 1901. Marconi perfected the spark-gap radio developed by Heinrich Hertz in the 1880s, which until the First World War was the most advanced technology to enable wireless communication between ships.
There are currently dozens of wireless technologies. One of the leading ones is the long-standing standardized ultra-wideband (UWB) technology. Like the WiFi and Bluetooth Low Energy technologies, this is a short-range wireless communication protocol that operates at a high frequency (up to 10 GHz) and over a wide spectrum, and allows much greater precision in locating objects, which sets it apart from the other aforementioned technologies.
UWB: advantages and benefits
Are you wondering why we use UWB in particular? Ultra-wideband technology is perfect for asset tracking solutions in businesses. In this application, UWB has several advantages. These include:
- Low power consumption while maintaining high bandwidth (500 MHz). UWB is therefore ideal for transferring more data from transmitters to other devices, achieving data transmission rates of seven to 27 megabits per second.
- Positioning based on time of flight, not on signal strength. This method involves measuring the time between sending a signal and receiving a feedback response to estimate the distance and calculate the position of the device. Thanks to its high accuracy (up to 0.5 m) and immunity to interference, UWB is ideal for use in harsh production conditions, as opposed to methods based on signal strength measurement.
- Greater immunity to interference in industrial environments. UWB achieves high real-time accuracy by sending up to a billion pulses per second, which equates to about one pulse per nanosecond.
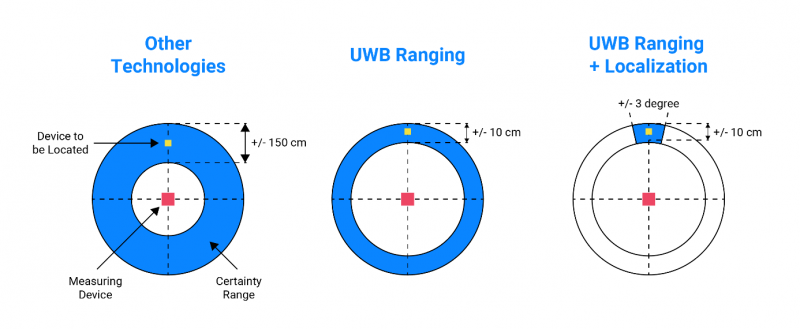
- The ability to specify range and location is a key differentiator for UWB compared to other technologies. A comparison of the accuracy of these parameters for UWB and competing technologies is set out below.
Use of UWB at Comarch
At Comarch, we use UWB technology widely in our proprietary Comarch Asset Tracking solution, with the help of which you can easily and safely optimize production processes in your company.
Asset location
Thanks to its ability to locate assets precisely, UWB technology makes it possible to read the position on the map with an accuracy of up to 0.5 meters, and thus to find assets immediately. This functionality can be particularly useful during annual inventories.
Production line monitoring
Defining digital zones makes it possible to detect monitored items in each zone, so the manager always knows where an item currently being manufactured is located. It is also possible to analyze the dwell time of a product at individual stations. The collected data can then be used to recreate the manufacturing process of a specific component, for example when monitoring quality or carrying out audits.
Material flow optimization
With the help of specialized analytical tools using UWB, it is possible to carry out detailed analysis of material flow paths between successive stages of production, which allows their optimization and increases process efficiency. In addition, defined alerts help eliminate bottlenecks.
Tool usage measurement
Lack of objective data on the actual use of mobile tools (such as forklifts) can lead to a waste of expensive resources. The use of UWB technology enables the creation of summary reports (for example, on total vehicle movement time per day) that make investment or funding reallocation decisions easier.
Buffer monitoring
Automatic counting of assets of a given type in buffer zones (the “supermarket” or “Kanban shelf”) allows monitoring of their filling level and notifies employees of the need to deliver more pieces or temporarily stop production.
Component picking verification
UWB technology-based asset tracking verifies whether the correct components are in their dedicated containers or at the designated production station before the job begins. This speeds up work significantly, and prevents manufacturing defects and downtime.
If you would like to learn more about our IoT ecosystem solutions, including the ultra-wideband-based Comarch Asset Tracking system, please visit www.comarch.com or write to us using the dedicated form.
Katarzyna Strzebońska, Comarch IoT









